Hyperthyroidism, also known as an overactive thyroid, is when the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormones. These hormones affect nearly every organ in your body and control many of your body's most important functions.
To understand more about hyperthyroidism, continue reading the article.
About hyperthyroidism
The thyroid gland is a small butterfly-shaped gland located in front of the trachea in the neck. The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate the way the body utilises energy. Therefore, these hormones affect most organs in your body, including your
heartbeat. With an excess of thyroid hormone, several bodily functions are accelerated.
An overactive thyroid may affect anyone, although it is approximately 10 times more prevalent in women than in men and often affects those between the ages of 20 and 40.
Signs & symptoms of hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism can cause various symptoms and may vary from person to person. The onset of symptoms might be gradual or sudden. While for some, the symptoms may be mild, for others, they may be severe and significantly affect their life.
Following are the common signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism:
Fast heart rate (tachycardia) - more than 100 beats per minute
Irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia)
Palpitation
Increased appetite
Nervous, anxious, and irritable
Mood swings
Trembling hands (tremors)
Increased sweating
Changes in menstrual patterns in women
Sensitivity to heat
Changes in bowel patterns, especially more frequent bowel movements
Fatigue
Muscle weakness
Difficulty sleeping
Goitre (visibly enlarged thyroid gland)
Warm skin
Hair thinning
Unexplained weight loss
Gynecomastia in male
Eyeball protrusion
Causes of hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland produces an excessive amount of thyroid hormones. This results in elevated levels of the two primary thyroid hormones, triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4).
Graves disease
Graves' disease is the leading cause and the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. It is an autoimmune disorder in which antibodies produced by your immune system stimulate the thyroid to become overactive.
Graves' disease has no known cause. However, it primarily affects young or middle-aged women who are genetically inclined. Additionally, smoking might raise your chance of developing it.
Thyroid nodules
This condition occurs when one or more nodules on the thyroid gland are overactive. Nodules are usually noncancerous (benign), although they may contain thyroid tissue, which can lead to excess production of thyroid hormones.
It is unclear why some develop thyroid nodules. However, those over 60 years old are typically affected.
Thyroiditis
It is the inflammation of the thyroid gland causing excess thyroid hormone to be produced.
Medication
Increased iodine levels in the body can cause the thyroid to produce excessive amounts of thyroid hormones. It may take several months for your thyroid hormone levels to return to normal after discontinuing a medicine that causes an overactive
thyroid.
Treatment of hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is usually treatable. The goal of treatment is to decrease thyroid hormone levels and manage the symptoms.
Anti-thyroid drugs
To reduce the symptoms of hyperthyroidism by preventing the thyroid gland from producing excess amounts of thyroid hormone.
Some of the drugs given include propylthiouracil and carbimazole.
Treatment with anti-thyroid drugs usually continues for at least a year or longer.
Beta Blockers
It can relieve symptoms such as tremors, fast heartbeat, and palpitations by reducing heart rate, although this medication does not affect thyroid levels.
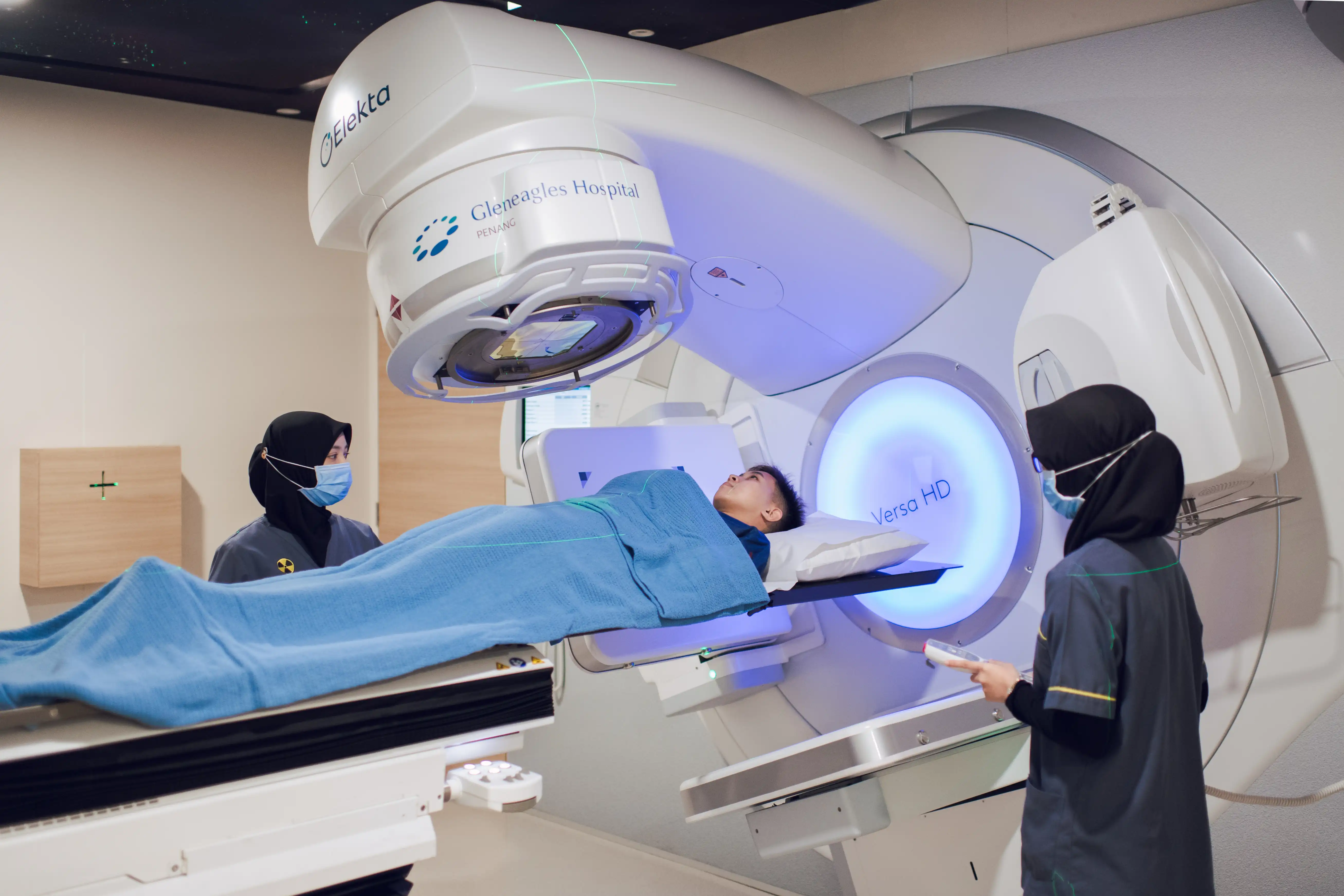
Radioactive Iodine Therapy
Used to destroy cells in the thyroid gland, which in turn decreases levels of thyroid hormones produced.
It is a highly efficient treatment for hyperthyroidism.
In this treatment, the patient will be given liquid or capsule containing low levels of radioactive substances and iodine that would be absorbed by the thyroid gland.
The majority of patients only need a single treatment. It may take a few weeks to months for full benefits.
A low dose of radiation is administered during the treatment.
Surgery
The removal of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy)is done to prevent a recurrence, if the thyroid gland is severely swollen or if other modes of treatment are unavailable.
To compensate for the absence of a thyroid gland, you would require medication lifelong.
Make an appointment at Gleneagles Hospitals
Early detection of hyperthyroidism makes treating the disease more effective with appropriate treatment. The caring and multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals are available for consultation and to provide the best care.
Get in touch with us to book an appointment with a specialist at Gleneagles Hospitals today. We assure you the best possible care tailored to your specific
needs.
References
National Health Service. Hyperthyroidism. Available at https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/overactive-thyroid-hyperthyroidism/
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Hyperthyroidism. Available at https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/endocrine-diseases/hyperthyroidism#radioiodine-therapy