The musculoskeletal system in the human body helps you to move and perform other everyday activities such as walking, jumping, and moving the body.
If left untreated, injuries to the any part of the musculoskeletal system (bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, tendons, cartilage) may lead to serious health complications.
Treatment options and procedures depend on the type of musculoskeletal or orthopaedic condition. At Gleneagles Hospitals, a multidisciplinary team of orthopaedic surgeons, physiotherapists, occupational therapists, and nurses work together to diagnose and treat your condition.
Arthroplasty is a surgical procedure to restore a joint's functionality by resurfacing bones and replacing it using an artificial joint called a prosthesis. This procedure is commonly done for osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease.
Arthroplasty may be recommended when medical treatments are insufficient to alleviate joint discomfort and/or disability. The most common sites for joint surgery are the hip and knees.
Total Hip Replacement

Hip replacement surgery may be needed when arthritis limits daily activities such as walking and bending, resting without pain, or moving or lifting the leg without stiffness. Hip replacement is recommended only after careful diagnosis of a joint problem. Read more
Hip arthroplasty or total hip replacement surgery involves replacing the femur (head of the thigh bone) and the acetabulum (hip socket) with artificial joint components.
The artificial femur part (ball and stem) is made of strong metal or ceramic, and the artificial socket is made of polyethylene (durable, wear-resistant plastic) or metal backed with a plastic liner. The ball and socket are designed to glide together to replicate the hip joint.
Conditions that damage the hip joint and may warrant a hip replacement surgery include osteoarthritis (a degenerative disease common that causes damage to the cartilage that covers the ends of bones and helps joints move smoothly) and rheumatoid arthritis (an inflammatory disorder that erodes cartilage and occasionally underlying bone, resulting in damaged and deformed joints).
This surgery is most likely needed when you have little pain relief from non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or if other treatments, such as physiotherapy, do not relieve hip pain.
Find out more about Arthroplasty versus Arthroscopy.
Total Knee Replacement
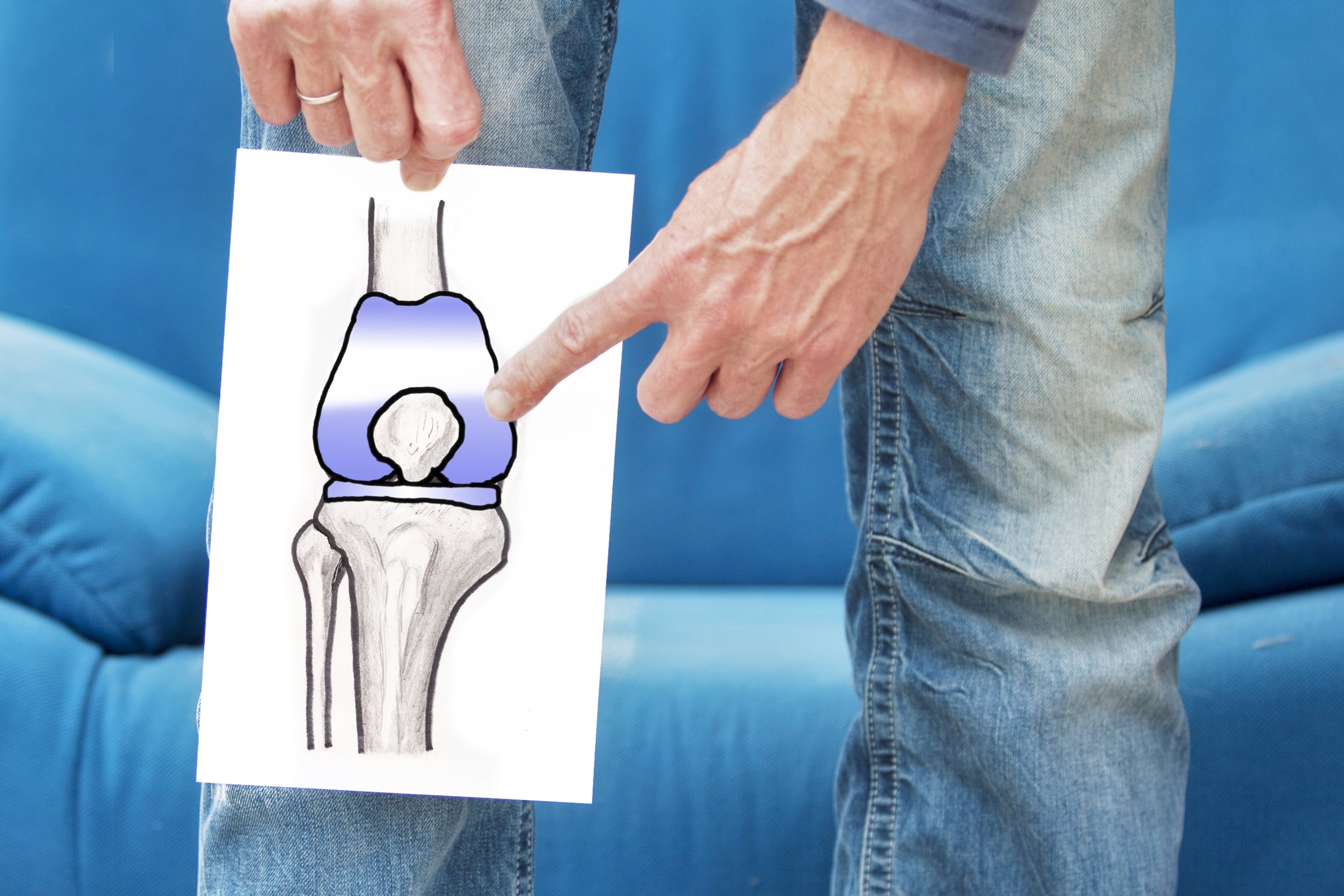
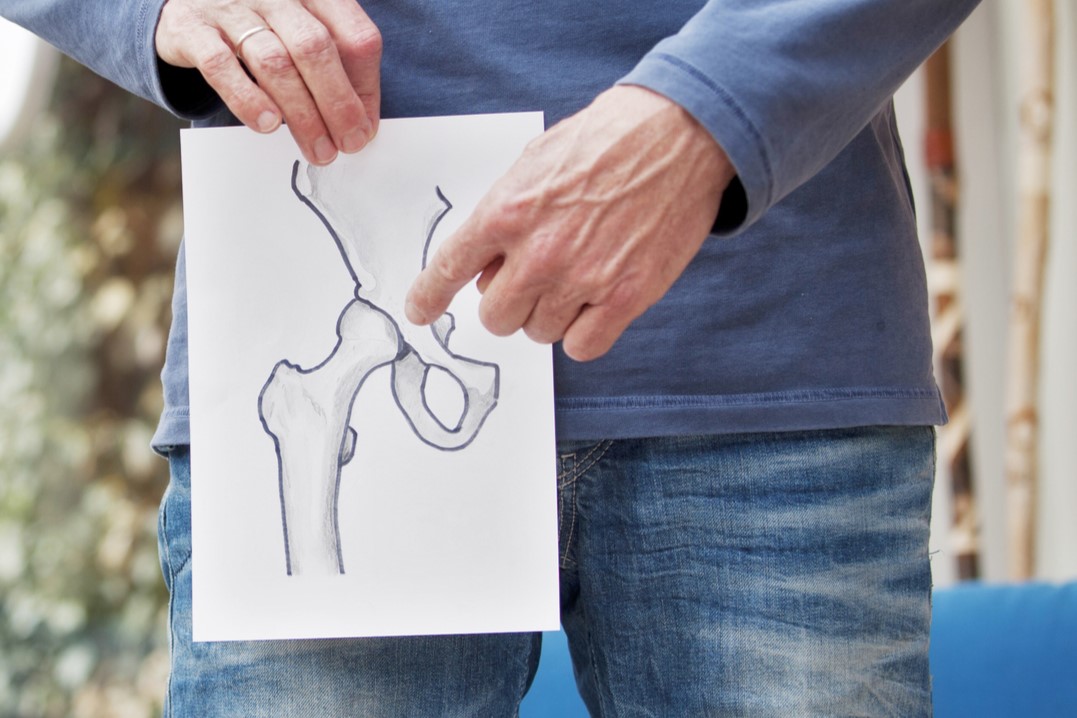
When knee pain caused by arthritis severely affect your ability to lead a full and active life, knee replacement surgery may be needed to help you return to your normal activities with less pain and greater freedom of movement. Read more
Artificial (total) knee replacement is a surgical procedure to replace the diseased (arthritic) parts of the joint with artificial joint components (prosthesis). These artificial joint components are usually the surfaces of the ends of the bones.
The main reason for replacing any arthritic joint with an artificial joint is to stop the bones from rubbing against each other and causing pain. Replacing the painful arthritic joint with an artificial joint gives the bones new surfaces, which move smoothly without causing pain.
Total knee replacement is done to replace a knee joint that is affected by a range of conditions including severe osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and post-traumatic arthritis, when an injury has damaged the knee.
Although knee replacement surgery is a common surgery for severe osteoarthritis of the knee, it should be done only after trying all the other treatment options available. It should be reserved as a salvage procedure when all other treatment modalities fail.
Find out more about Arthroplasty versus Arthroscopy.
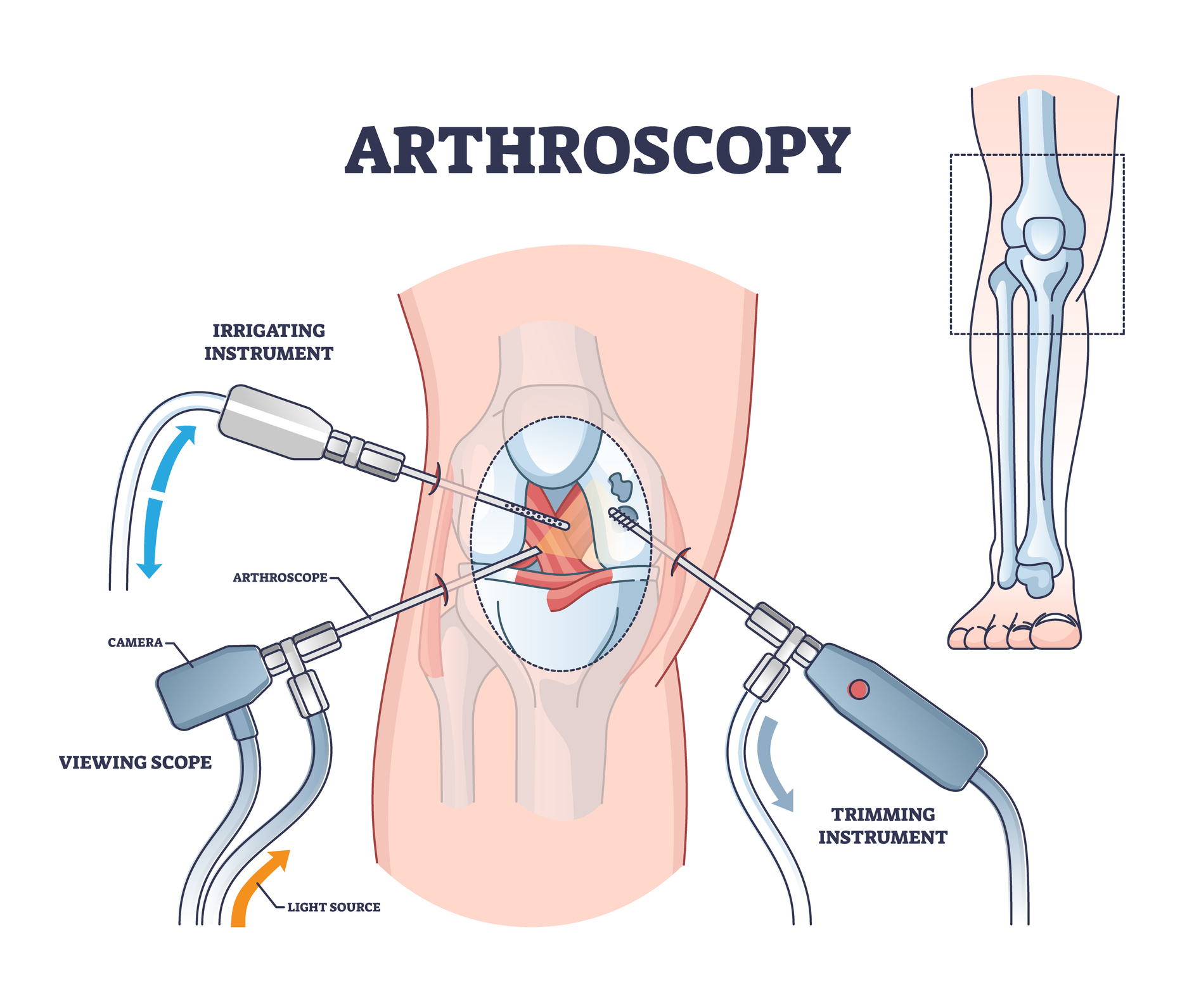
Arthroscopy or arthroscopic surgery is a keyhole surgical procedure used to examine or repair joints or replace a damaged meniscus (the C-shaped discs that cushion the knee).
In this keyhole surgery, small incisions are made in your body, and a tiny camera is inserted. The images are presented on a screen, and a device is used to correct the condition. Read more
- Knee arthroscopy
Knee arthroscopy is a surgical technique that aid in the diagnosis and treatment of the knee joint. The procedure involves a small incision, and the insertion of a tiny camera called an arthroscope into the knee. This enables the surgeon to visualise the problem in the knee and, if necessary, correct the issue using small instruments through another small incision.
Knee arthroscopy can be done as an outpatient procedure (day surgery) so you will go home on the same day. The small wounds from the arthroscopy are less painful than those from open surgery. Their appearance is also more cosmetically pleasing.
- Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction surgery
ACL reconstruction is a surgical tissue graft replacement of the anterior cruciate ligament, located in the knee, to restore its function after an injury. In this procedure, a ligament is constructed using a tendon to replace the ACL. The torn ligament can either be removed from the knee or preserved before reconstruction.
- Subacromial decompression
An arthroscopic procedure is done to release the tight coracoacromial ligament and to remove bone tissue in the subacromial space.
Find out more about Arthroplasty versus Arthroscopy.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that causes pain, numbness, and tingling in your hands and fingers because the median nerve is compressed and squeezed.
Carpal tunnel release is usually recommended if you have experienced symptoms such as pain, numbness, and tingling sensation on a moderate to severe degree that lasts six months or longer.This minor procedure can be performed as day surgery under local anaesthesia.
- Open carpal tunnel release: A small incision is made in the wrist and the transverse carpal ligament is cut to ease the pressure on the median nerve.
- Endoscopic carpal tunnel release: During this minimally invasive carpal tunnel surgery,the surgeon makes a small incision in the wrist and inserts an endoscope (a camera attached to a narrow tube) to view the inside of your wrist. A special knife is then used to cut the transverse carpal ligament similar to the open carpal tunnel release.
A trigger finger is a condition where one or more of the tendons in the finger are affected and causes pain or stiffness when straightening or bending the finger. The affected finger may become ‘locked’ or stuck in a bent position.
Trigger Finger surgery may be suggested if all other types of treatment have not worked, and the affected finger is locked (permanently stuck). There are two surgical options open trigger finger release and percutaneous trigger finger release surgery
Trigger finger surgery is performed to release the tendon from the sheath when it is causing pain, or the finger becomes ‘locked’. The surgeon will make a small incision near the base of the affected finger to release the tendon from the part of the sheath it was catching on. Both surgeries only require local anaesthesia, and you would be able to return home the same day.
A tendon from one of your healthy fingers would be detached and reattached to the affected finger. This is done to restore function following muscle or tendon dysfunction due to nerve or muscle injury or neuromuscular defect.
A corrective spine osteotomy is a surgical procedure to correct spinal deformities and restabilise the spine. The procedures include:
- Posterior spinal fusion
- Anterior spinal fusion
- Growth modulation techniques – vertebral body tethering
Corrective osteotomy will reduce any pain and/or nerve compression. A more upright posture will make you feel less tired, as your upper body is now supported by a straighter spine. Your straighter spine will also improve your physical appearance.
A discectomy is performed to treat herniated or slipped discs in the spine. This surgical procedure involves the removal of the fragment of the disc which is exerting pressure on the nerve. This can be done as an open surgery or keyhole surgery.
Laminectomy is a surgical procedure that relieves pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots caused by spinal stenosis. Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of the spinal canal resulting in pressure in the spinal cord. This causes pain, weakness, or numbness in your back, legs, arms, and neck.
This surgical procedure removes tissue and bone exerting pressure on the spine. It is also used to treat spinal injuries, herniated discs, and spinal tumours.
Depending on the type, location and severity of the fracture, a range of techniques are used to ensure that the bones are healing and stable to retain function. This may include immobilisation and the insertion of pins, plates, wires, and screws.
Amputation is the surgical removal of all or part of a limb or extremity, such as an arm, leg, foot, hand, toe, or finger.
Surgical removal, as in the excision of a tumour.
Often, non-surgical treatments are also recommended. These include:
- Specific exercises to improve strength, range of motion and flexibility.
- Immobilisation to prevent extra strain on a particular area so that it has a chance to heal. Examples include the use of casts, braces, and splints.
- Medications to relieve pain and swelling.
- Lifestyle changes such as a change in diet, activity and even the way you exercise to prevent injuries from reoccurring
A wide range of rehabilitation services are available to restore physical, mental and life skills for patients who may have reduced function in their daily activities.
The goal of rehabilitation is to enhance and restore functional ability and quality of life for those with physical impairments or disabilities. Return to function can be achieved via a few methods; with physiotherapy and occupational therapy being at the forefront.
Physiotherapy deals with returning and improving regular bodily movement with focus on a specific body part, while occupational therapy aims to return the affected individual to their daily routine with focus on ability to complete tasks and activities.
Speak to your doctor to know more about the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment for orthopaedic conditions. The caring and multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals are available for consultation and to provide the best care.
Get in touch with us to book an appointment with an Orthopaedic specialist at Gleneagles Hospital today.
Discover the range of comprehensive Orthopaedic treatments and services at Gleneagles Hospitals.
If you encounter a situation that requires medical attention, please seek immediate medical attention at the Accident and Emergency (A&E) department at your nearest Gleneagles Hospital.