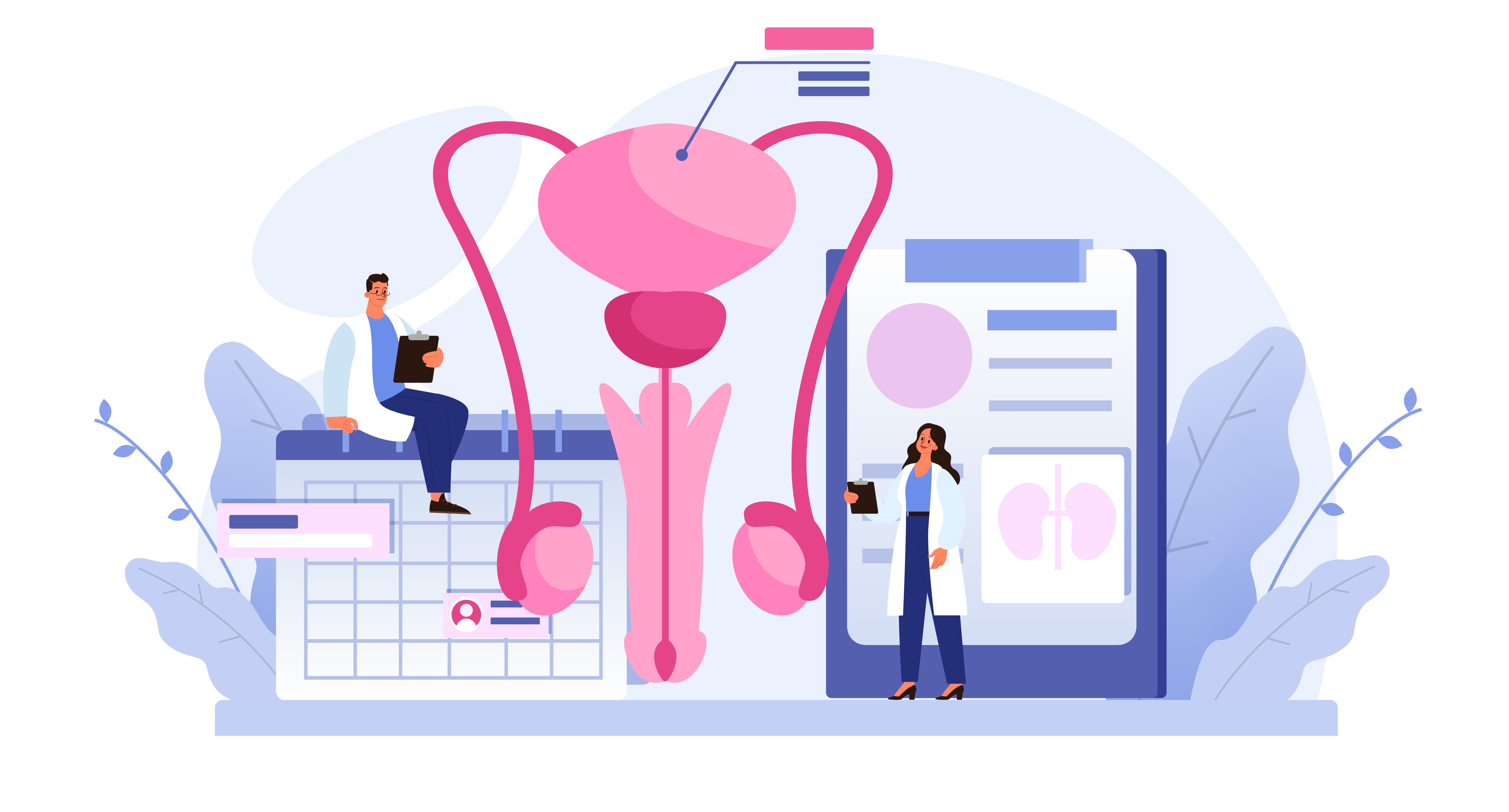
Urodynamics
Urodynamics is a study that assesses how well the bladder and urethra store and release urine.
It is important to note that some prescribed treatments are not as effective as others as doctors advocate treatment based on their patient's complaints. Unfortunately, these symptoms are often subjective, and doctors may not arrive at the root cause.
Dr Warren Lo, a consultant urologist in Gleneagles Hospital Kuala Lumpur, discusses more about urodynamics and runs through five patient scenarios that are commonly seen by urologists.
Investigating with Urodynamics
Urodynamics consists of a range of tests to assess the function of the urinary tract. Urodynamics investigations can clearly show the bladder's various conditions such as overactivity or underactivity, besides identifying the underlying causes for various types of urine leaks. They also pinpoint urinary obstructions and reflux conditions, which are risky to the kidneys.
Urodynamics is recommended for various bladder dysfunctions secondary to spinal cord injuries, brain pathologies such as stroke, Parkinson's disease, and other unresolved bladder conditions. It is also indicated for paediatric congenital spinal conditions such as spinal bifida and myelomeningocele.
The investigation involves a relatively simple procedure. Tiny catheters are inserted into the bladder and anus to assess the bladder capacity, pressure, stretchability, sensation, and various stages of leakage. The reflux of urine into the kidneys and bladder outlet obstructions can be clearly shown in this test.
Urodynamics is also indicated for patients who have had previous operations for urine leaks but still persistently leak post-op. For bladder dysfunction and prostate enlargement patients, it is valuable to determine whether the prostate surgery will benefit the patient as sometimes the patient may not be able to pass urine even after an operation due to a weak bladder.
Urodynamic tests do not involve anaesthesia and usually take 30 to 45 minutes to complete. The test is not painful or causes much discomfort, although the patient may feel the catheter being inserted. It is usually done as a daycare procedure with the patient will be discharged on the same day.

Let's examine these five examples to illustrate the value of a urodynamics test.
| SCENARIO 1 |
| I was diagnosed with recurrent urinary tract infection (UTI) 5 years ago. But strangely, most urine test results are negative. During that time, various doctors have given me multiple antibiotics. However, the urgency and frequency of urination have never gone away. Is there anything wrong with me? |
- This patient may suffer from an overactive bladder but is often treated as a UTI. This is because most patients experiencing UTIs may present with some degree of urgency and frequency. If the urine tests repeatedly indicate a negative culture, one should consider an overactive bladder which can be easily determined by urodynamic tests. The appropriate treatment, in this case, would be a bladder relaxant rather than antibiotics.
| SCENARIO 2 |
| I was diagnosed with an overactive bladder as I often present with urinary urgency and cannot hold my urine for longer than an hour. I have been treated with various drugs for my overactive bladder. However, the problem seems to worsen every time I take my medications. |
- In this scenario, some patients who present signs of overactive bladders may instead have underactive bladders. As they are unable to empty their bladders, there will always be residual urine within. The bladder will gradually fill up whenever the patient drinks and with a limited bladder capacity left due to the residual urine, the bladder will get overstretched, leading to symptoms of urgency and frequency like an overactive bladder. By giving bladder relaxant medications, it will further worsen the underactive bladder and ultimately results in urine leak caused by overflow. The only way to confirm the underactive bladder is through urodynamics.
| SCENARIO 3 |
| I had four uneventful vaginal deliveries. My babies were healthy, but I have since suffered from urine leaks. I was informed that I suffered from urinary incontinence because of my weak pelvic floor muscle. I went through six months of intensive physiotherapy, but the problem persists. |
- As the lady presented with urine leaks after multiple deliveries, the doctor could be misled into thinking the patient is suffering from stress urinary incontinence, usually due to a weakened pelvic floor muscle. Instead, the patient could suffer from an overactive bladder with urgent urine leaks or a combination of both urge and stress urine leaks, even though she has only been treated for stress urine leaks. In this scenario, the pelvic floor exercise may not be adequate. Again, a urodynamic test would indicate whether the patient suffers from stress, urge urine leak, or a combination of both.
| SCENARIO 4 |
| I was diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease three years ago and began to experience issues with urinary incontinence. I was told it was related to my prostate enlargement. After taking prostate medications for three months, the leaking was gotten worse. I am concerned. |
- Elderly patients will often present with urine obstruction secondary to prostate enlargement. However, patients with Parkinson's disease often present some degree of urine urgency and are unable to empty the bladder due to underlying neurogenic underactive bladder conditions. Giving the patient prostate medications will not solve the underlying bladder issues. The patient will need a urodynamic test to determine the bladder condition as prostate enlargement could be just one of the problems that they have. As the problem lies in the bladder rather than the prostate, an accurate assessment can prevent the patient from undergoing unnecessary prostate surgery.
| SCENARIO 5 |
| Recently, I was involved in a traffic accident and now suffer from an incomplete spinal cord injury. I have issues with recurrent urinary tract infections. I feel I am unable to empty my bladder, but doctors just continue to prescribe antibiotics for me. I think something is not right. |
- A spinal cord injury patient experiences various bladder dysfunction issues from a severe overactive bladder to an underactive bladder depending on the level of injury. When they are not able to empty the bladder properly, they will always have residual urine within the bladder, eventually leading them to recurrent UTIs. Urodynamic investigations will help to differentiate which type of bladder condition the patients suffer from.
Getting Tested
The importance of urodynamics testing cannot be over-emphasised. It is invaluable for various types of bladder dysfunctions which are often overlooked or understated. Urinary problems can be sensitive, and many urinary complaints can be subjective and present differently from what they really are. In this situation, nothing could be more helpful than being able to pinpoint the source of the problem as well as investigate the underlying causes. Urodynamics testing provides this platform. Speak to your urologist if you have persistent bladder issues that cannot be resolved – identifying the root cause through urodynamics would help to put you on the right treatment plan.
Written by
Dr Warren Lo Hwa Loon
Consultant Urologist
Gleneagles Hospital Kuala Lumpur