Topics
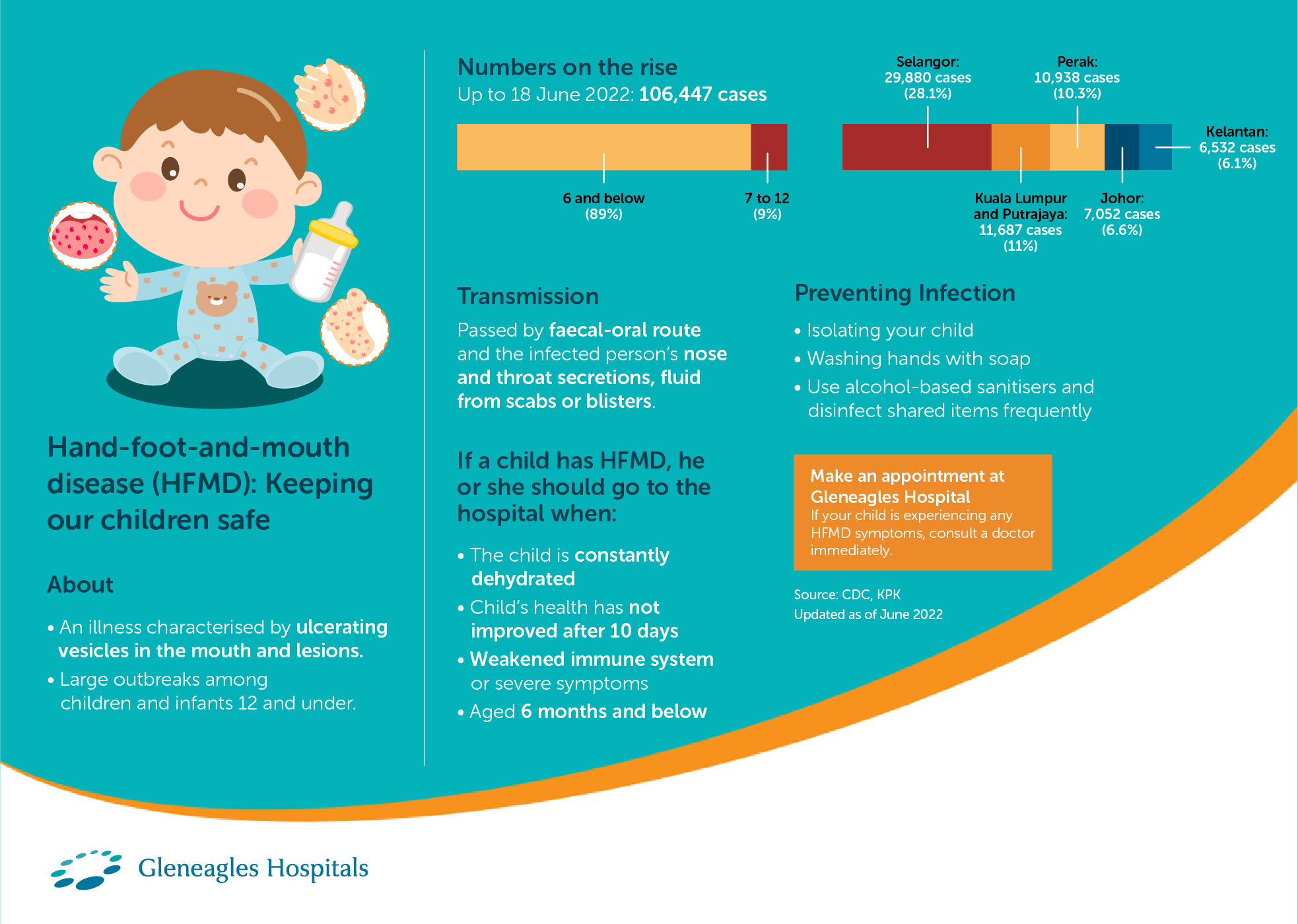
In Malaysia, hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) is a general public concern because this endemic disease can result in large outbreaks and deaths among children and infants.
Up to 18 June 2022, approximately 106,447 HFMD cases were recorded. 89% of the cases were recorded among children aged 6 and below while 9% were among those aged between 7 and 12.
- Selangor: 29,880 cases (28.1%)
- Kuala Lumpur & Putrajaya: 11,687 cases (11%)
- Perak: 10,938 cases (10.3%)
- Johor: 7,052 cases (6.6%)
- Kelantan: 6,532 cases (6.1%)
The majority of outbreaks occurred at:
- Nurseries and preschool: 56%
- Household: 40%
- Day-care centres: 3%
About hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD)
Hand-foot-and-mouth (HFMD) is a common infectious disease seen in children and infants. The disease is usually mild and self-limiting. Symptoms include fever, sore throat, mouth sores, and skin rash with blisters on arms, legs, and buttocks.
HFMD is caused by viruses, and the individual infected with HFMD is contagious. The virus spreads from person to person through faecal-oral route and the infected person's nose and throat secretions, fluid from scabs or blisters.
An individual with HFMD is most contagious during the first week of illness.
When should a child with HFMD go to the hospital
- When the child is not drinking enough water
- When the child’s condition is not improving after 10 days
- If the child has a weakened immune system
- If the child has severe symptoms such as high fever with chills
- If the child is younger than 6 months
Preventing HFMD infection
- Wash your hands with soap and water, especially after using the toilet, changing diapers, before preparing food and before eating.
- Use an alcohol-based sanitiser if soap and water are not available.
- Disinfect touched surfaces and shared items frequently.
- Avoid touching the face with unwashed hands.
- Avoid close contact with individuals who are sick.
- Ensure the child stay at home if he or she is showing symptoms.
Make an appointment at Gleneagles Hospital
If your child is experiencing symptoms of HFMD, please consult your child’s doctor or paediatrician.













.webp?sfvrsn=a6d32366_7)







































.webp?sfvrsn=91e22b26_8)












