This Might Interest You
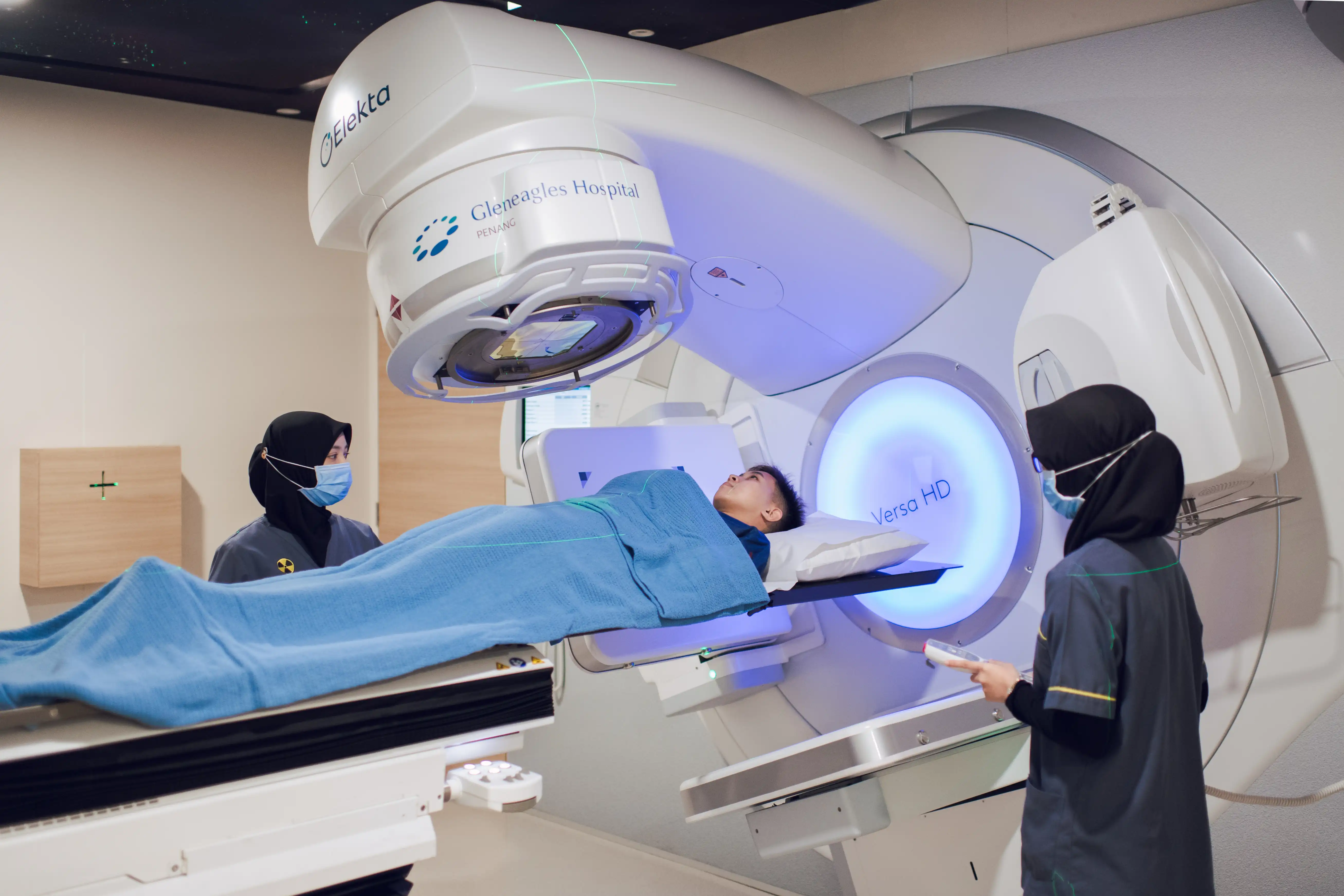
In conclusion, our dedication to leveraging cutting-edge technology, coupled with our team of experienced staff, advanced treatment facility and meticulous treatment planning, guarantees the highest s...

What is jaundice? Jaundice is yellow colour of the skin and whites of the eyes that is common in newborn babies. It is caused by accumulation of bilirubin, a breakdown product of red blood cells ...
Yellow fever is a viral infection that can be spread from mosquito to human, usually affecting kidney and liver. It is found only in parts of Central and South America and Sub-Saharan Africa. Se...

While drinking coffee on an empty stomach can have potential downsides for some individuals, it is not universally harmful. Sensitivity to caffeine, overall health, and individual nutrition needs are ...

Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the joints, causing swelling, stiffness, and pain. It can also harm other parts of the body. However, with early diagnosis, ...

A Neutropenic diet is a low bacteria diet that safeguards individuals with weakened immune systems due to reasons like transplant procedures, cancer treatment, viral infections, and aplastic anemia. A...


